

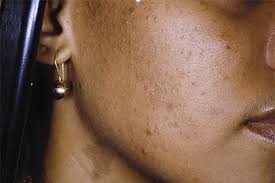
Tinea versicolor is a common skin condition due to overgrowth of a skin surface yeast. This overgrowth results in uneven skin color and scaling that can be unsightly and sometimes itch. The yeast normally lives in the pores of the skin and thrives in oily areas such as the neck, upper chest, and back. Tinea versicolor has small, scaly white-to-pink or tan-to-dark spots which can be scattered over the upper arms, chest and back. They may sometimes appear on the neck and the face. On light skin, Tinea versicolor may be faint or can appear as tan-to-pink spots, while on dark skin Tinea versicolor may be light or dark. The fungus grows slowly and prevents the skin from tanning normally. As the rest of the skin tans in the sun, the pale spots, which are affected by the yeast, become more noticeable, especially on dark skin.
Tinea versicolor has small, scaly white-to-pink or tan-to-dark spots which can be scattered over the upper arms, chest and back. They may sometimes appear on the neck and the face. On light skin, Tinea versicolor may be faint or can appear as tan-to-pink spots, while on dark skin Tinea Versicolor may be light or dark. The fungus grows slowly and prevents the skin from tanning normally.
Tinea Versicolor usually produces few symptoms. Occasionally, there is some slight itching that is more intense when a person gets hot.
Most people get tinea versicolor when they are teenagers or young adults. It is rare in the elderly and children, except in tropical climates where it can occur at any age. Both dark and light skinned people are equally prone to its development. People with oily skin may be more susceptible than those with naturally dry skin.
The yeast is normally present in small numbers on everyone's skin. Anyone can develop an overgrowth of yeast. During the summer months when the temperature and humidity are high, the yeast can increase. The excess yeast on the skin prevents the normal pigmentation process, resulting in light and dark spots. In tropical countries with continuous high heat and high humidity, people can have these spots year round. In other climates, the spots generally fade in the cooler and drier months of the year. Why some people get tinea versicolor and others do not is unclear.
In tropical countries with continuous high heat and high humidity, people can have these spots year round. In other climates, the spots generally fade in the cooler and drier months of the year.
Although the light or dark colored spots can resemble other skin conditions, tinea versicolor can be easily recognized by a dermatologist. In most cases, the appearance of the skin is diagnostic, but a simple examination of the fine scales scraped from the skin can confirm the diagnosis. Scales are lightly scraped onto a slide and examined under a microscope for the presence of the yeast. A special light may help to make the diagnosis by showing a yellow green color where the skin is affected.
Tinea versicolor is treated with topical or oral medications. Topical treatment includes special cleansers including some shampoos, creams, or lotions applied directly to the skin.
Several oral medications have been used successfully to treat tinea versicolor. Because of possible side effects, or interactions with other medications, the use of these prescription medicines should be supervised by a dermatologist. After any form of treatment, the uneven color of the skin may remain for several months after the yeast has been eliminated until the skin repigments normally.
Tinea versicolor may recur. Special cleansers may decrease episodes when used once or twice a month, especially during warm humid months of the year.
Each patient is treated by the dermatologist according to the severity and location of the disease, the climate, and the desire of the patient. It's important to remember that the yeast is easy to kill, but it can take weeks or months for the skin to regain its normal color.
Telangectasias (commonly known as spider veins) are dilated or broken blood vessels located near the surface of the skin. They often occur on the face and particularly on the sides of the nose. They often look like small red or pink lines, which temporarily whiten when pressed.
Some Symptoms Of Spider Veins Include:
Common Causes of Spider Veins
Spider veins are generally caused by weak or damaged valves. The following causes can contribute to weaker blood flow in certain areas of your body.
Treatment(s):
Thankfully, laser therapy is safe and efficacious treatment. It is an easy in-office treatment that can be performed during ones lunch break. In 10 minutes those red lines are gone and you can go right back to work. No wound care or dressings needed.
Sclerotherapy is also a treatment option. A special solution is injected directly into the affected veins, forcing the veins to close and the blood to redirect into healthier veins. The old vein turns into scar tissue that your body will eventually absorb, causing it to fade.
Lately, the decision to obtain a tattoo has become increasingly popular, and so has the decision to remove them! DON'T REGRET IT ... REMOVE IT! An estimated 20 million Americans have tattoos, and many of them now feel that having a tattoo does not fit their image. Those remorseful about their tattoos are consulting with cosmetic laser physicians to determine if the removal of their tattoo is possible. Today's advanced laser technology provides the means for tattoo removal safely and quickly and, in most cases, without leaving a scar. Complete removal of all types of tattoos, on all skin types, in up to half the treatments.
Cosmetic medical lasers designed to eradicate tattoos range from a single wavelength of light to a broad spectrum of light, the varieties of which are intended to obliterate the ink in the tattoo without damaging the skin. Certain colors of light are absorbed by specific corresponding colors of the tattoo ink. The light energy vaporizes or fragments the ink particles. Your body then absorbs these ink fragments naturally and the color fades over the next couple of weeks. This treatment is very similar to methods used for years to treat birthmarks.
Ask us about our "Cosmetic Consultation Reimbursement" policy offered to all patients. Come discuss your needs and goals with Dr. Robinson and the office visit cost will be applied to future costs for the discussed procedure. Procedure must be completed within 30 days of your consult visit.
Subcission is a treatment used to correct a type of scar called a valley scar. A valley scar simply means there is a defect in the volume of the skin at the site of the scar. The goal of subcission is to improve this decreased volume. This then allows a depressed scar to regain its smooth appearance. This treatment may be combined with other scar treatments to yield the best cosmetic results.
Spider Veins are very small veins caused by a dilation of the small venules under the skin. This occurs when the pressure inside the vein increases enough to overcome normal resistance of the vein wall. The ability of veins to resist increased pressure is reduced with hormonal changes.
Reticular Veins are small, bluish-colored veins that carry blood to the skin venules and are larger than spider veins. These veins have thin walls and dilate with excessive venous pressure. When this occurs, they become large enough to be unsightly, but are not considered to be varicose veins.
In recent years medical lasers have made great advancements in sophistication. Today, lasers are safely used for a wide variety of cosmetic non-invasive treatments. Laser Therapy treatment is extremely safe and effective on leg veins, as well as veins visible on the face, neck, and chest. Laser treatment also corrects benign pigmented lesions such as age spots and birthmarks. These non-invasive treatments are increasingly popular because they have very few side effects, and one can resume regular activities immediately following treatment.
Both men and women, light and dark-skinned individuals can now safely and effectively benefit from laser therapy for spider veins. Patients using blood thinners or afflicted with a serious illness generally are not candidates for treatment. Patients with dark suntans or photosensitivity disorders, uncontrolled or severe diabetes, bleeding disorders, or those currently taking photosensitizing medications may also be restricted from candidacy.
The number of treatments necessary to resolve your vein concerns depends on the size of the vein and your body's ability to heal. During your consultation, you will be given an estimate of the number of treatments required to obtain optimal results.
Treatment may vary from 15 to 30 minutes. As a result of treatment, the walls of the veins are damaged by the laser's heat. The body next induces a healing process. The veins shrink and become less visible or disappear altogether. Medical studies have documented exceptional results on veins with laser treatments.
The beauty of this treatment is that there is no down time involved. You can resume most of your regular activities immediately. Your doctor may use various methods to reduce the pain that may be associated with this procedure. Swelling and mild bruising can occur, but almost always resolve over a short period of time. Limiting sun exposure, avoiding strenuous exercise, and wearing compression stockings will greatly minimize the risk of complications immediately following your treatment.
Laser Therapy treats many types of leg veins, including shallow spider veins and reticular veins.
Spider Veins are very small veins caused by a dilation of the small venules under the skin. This occurs when the pressure inside the vein increases enough to overcome normal resistance of the vein wall. The ability of veins to resist increased pressure is reduced with hormonal changes.
Reticular Veins are small, bluish-colored veins that carry blood to the skin venules and are larger than spider veins. These veins have thin walls and dilate with excessive venous pressure. When this occurs, they become large enough to be unsightly, but are not considered to be varicose veins.
Schedule an office visit to discuss your concerns and skincare goals with Dr. Robinson and the office visit cost will be applied to the future cost for the "consulted procedure". The "consulted procedure" must be completed within 30 days of your consult visit.
Just like a precious piece of jewlery or a beautiful piece of furniture, the skin can become dull, weathered and aged. With the modern age of dermatology one can restore the brightness, alleviate lines, get rid of dark marks, erase broken capillaries and scars with no social downtime and superior cosmetic results.
Cosmetic Consultation Reimbursement policy offered to all patients. Schedule an office visit to discuss your concerns and skincare goals with Dr. Robinson and the office visit cost will be applied to the future cost for the "consulted procedure". The "consulted procedure" must be completed within 30 days of your consult visit.
Seborrheic Keratoses are often confused with warts or moles, but they are quite different. Seborrheic Keratoses are non-cancerous growths of the outer layer of skin. There may be just one growth or many which occur in clusters. They are usually brown, but can vary in color from light tan to black and range in size from a fraction of an inch in diameter to larger than a half-dollar. A main feature of Seborrheic Keratoses is their "waxy, pasted-on" appearance. They sometimes look like a dab of warm brown candle wax that has dropped onto the skin or like barnacles attached to the skin.
The exact cause of seborrheic keratoses is unknown; however, they seem to run in families. They are not caused by sunlight and can be found on both sun-exposed and non sun-exposed areas. Seborrheic Keratoses are more common and numerous with advancing age. Although Seborrheic Keratoses may first appear in one spot and seem to spread to another, they are not contagious.
Anyone may develop Seborrheic Keratoses. Some people develop many over time, while others develop only a few. As people age, they may simply develop more. Children rarely develop Seborrheic Keratoses. Seborrheic Keratoses may erupt during pregnancy, following estrogen therapy, or in association with other medical problems.
Seborrheic Keratoses are most often located on the chest or back, although they also can be found on the scalp, face, neck, or almost anywhere on the body. The growths usually begin one at a time as small, rough, itchy bumps which eventually thicken and develop a warty surface.
Seborrheic Keratoses are benign (non-cancerous) and are not serious. Unless they develop suddenly, they do not indicate a serious health problem. They may be unsightly, especially if they appear on the face. Removal may be recommended if they become large, irritated, itch, or bleed easily. A Seborrheic Keratosis may turn black and may be difficult to distinguish from skin cancer. Such a growth must be removed and biopsied (studied under a microscope) to determine if it is cancerous or not.
Creams, ointments, or other medication can neither cure nor prevent Seborrheic Keratoses. Most often Seborrheic Keratoses are removed by cryosurgery, curettage, or electrosurgery. Cryosurgery, liquid nitrogen, a very cold liquid gas, is applied to the growth with a cotton swab or spray gun to "freeze" it. A blister may form under the growth which dries into a scab-like crust. The Keratosis usually falls off within a few weeks. Occasionally, there will be a small dark or light spot that usually fades over time.
Curettage: The keratosis is scraped from the skin. An injection or spray is first used to anesthetize (numb) the area before the growth is removed (curetted). No stitches are necessary, and the minimal bleeding can be controlled by applying pressure or the application of a blood-clotting chemical.
Electrosurgery: The growth is anesthetized (numbed) and an electric current is used to burn the growth which is then scraped off.
Today, there are many treatment options which, when properly chosen for the specific type of scar and/or skin type, can greatly improve and repair your skin to its natural and more healthy state. These treatment options include surgical excision, laser skin resurfacing, laser skin rejuvenation, intense pulsed light skin rejuvenation, microdermabrasion, chemical peels, dermabrasion, cortisone injections, and bleaching or age defying softening topicals.
During your consultation, your skin type and scar will be evaluated and a customized treatment program will be developed. This may include a combination of treatments to optimize your results. In some cases, certain types of scars can only be improved and not completely eliminated. Your treatment expectations and results will be thoroughly discussed during your consultation.
This option is typically for scars that are deeply pitted, raised, or for older surgical scars that did not heal properly. The scar tissue is removed, followed by careful stitching of the skin to leave a much smaller or thinner scar line.
This treatment is excellent for acne scarring as well as sun damaged or aged skin. The laser vaporizes the damaged skin and commences the regeneration of fresh skin during the following weeks. The thermal damage to the deep tissue stimulates new skin growth, promoting a healthy new collagen layer as well.
Microdermabrasion is a non-surgical exfoliating treatment helpful for those unhappy with scars, acne scars, sun-damaged skin, pigmentation spots, stretch marks, fine lines, and rough skin. Treatment can be performed anywhere on the body. This treatment works for scarring especially when used in conjunction with other modalities.
This is a non-invasive approach in which the laser energy penetrates the skin, damaging the deepest tissue layers. The damage causes the skin to repair itself and stimulates the production of collagen. As the underlying skin thickens, the top layers of the skin begin to contour more smoothly. Multiple treatments may be recommended. This treatment option works well in conjunction with microdermabrasion for certain scars.
Depending on the skin type and scar to be treated, a superficial, medium, or deep chemical peel may be recommended. In addition to removing the top layers of the epidermis, chemical peels are noted for their ability to stimulate collagen synthesis and aid in the production of new skin cells. Depending on the type of peel, multiple treatments may be required.
This is a non-invasive approach in which intense pulsed light energy penetrates the skin, damaging the deepest tissue layers. The damage causes the skin to repair itself and stimulates the production of collagen. As the underlying skin thickens, the top layers of the skin begin to contour more smoothly. Multiple treatments may be recommended. This treatment option works well in conjunction with microdermabrasion for certain scars and coarse, uneven skin texture.
By the time we reach our adult years, our skin has been exposed to rough childhood environmental damage, acne, chicken pox, scrapes, burns and numerous other phenomena. As part of the skin’s natural healing process, a scar is formed when several layers of the skin have been damaged. Presently there are diverse treatment modalities available to address various forms of skin scarring. These treatments can dramatically reverse, improve, and renew your skin to it’s natural, healthier state. Many patients seek solutions not only to achieve healthy-looking skin, but also to improve their image and self esteem.
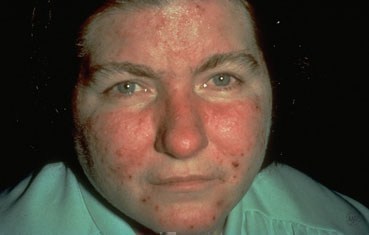
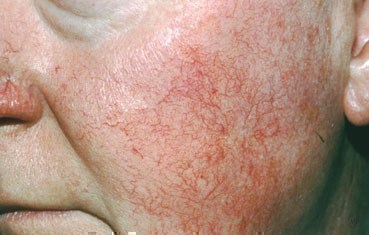
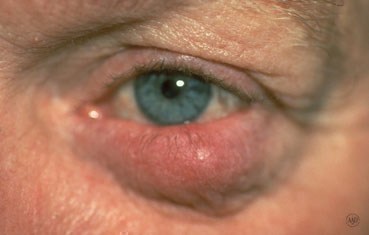
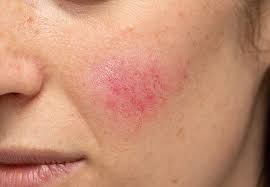
Rosacea is a common skin disease that causes redness, papules, and swelling on the face. Often referred to as adult acne, rosacea frequently begins as a tendency to flush or blush easily. It may progress to persistent redness in the center of the face that may gradually involve the cheeks, forehead, chin, and nose. The eyes, ears, chest, and back may also be involved. With time, small blood vessels and tiny pimples begin to appear on and around the reddened area; however, unlike acne, there are no blackheads.
When rosacea first develops, the redness may come and go. Some people may flush or blush and never form pustules or papules. Small dilated vessels may also be present. However, when the skin doesn't return to its normal color, and when other symptoms such as pimples and enlarged blood vessels become visible, it's best to seek advice from a board-certified dermatologist. The condition may last for years, rarely reverse itself, and can become worse without treatment.
Small red bumps, some of which may contain pus, appear on the face. These may be accompanied by persistent redness and the development of many tiny blood vessels on the surface of the skin.
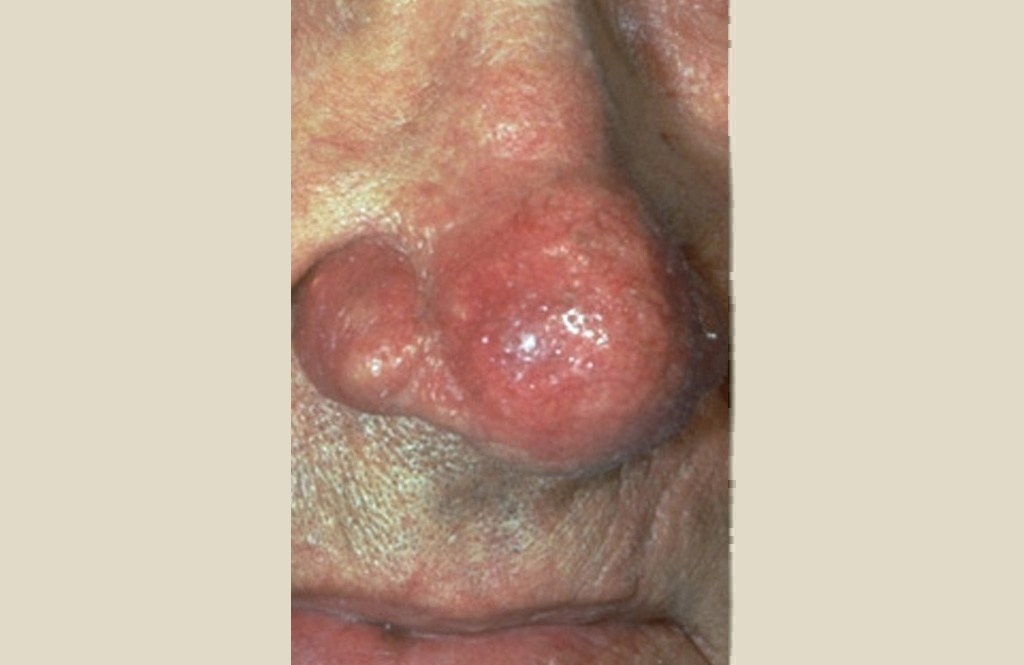
In more advanced cases, a condition called rhinophyma may develop. The oil glands enlarge causing a bulbous, red nose, and puffy cheeks. Thick bumps may develop on the lower half of the nose and nearby cheeks. Rhinophyma occurs more commonly in men.
Anyone can get Rosacea. It is more common in fair skinned adults between the ages of 30 and 50. Since it may be associated with menopause, women are affected more often than men and may likely have an extreme sensitivity to cosmetics. In people of color, studies show that early symptoms can often be missed and may be under diagnosed because dark skin can mask facial redness. Few children get rosacea, but it is worth considering if the signs and symptoms are there.
Tips for Rosacea Patients
Many people with Rosacea are unfamiliar with it and do not recognize it in its early stages. Identifying the disease is the first step to controlling it. Self-diagnosis and treatment are not recommended since some over-the-counter skin products may make the problem worse.
Dermatologists often recommend a combination of treatments tailored to the individual patient. These treatments can stop the progress of rosacea and sometimes reverse it.
The key to successful management of Rosacea is early diagnosis and treatment. Rosacea can be treated and controlled if medical advice is sought in the early stages. When left untreated, Rosacea will get worse and may be more difficult to treat.
Everyone has moles, sometimes 40 or more. Most people think of a mole as a dark brown spot, but moles have a wide range of appearance. At one time, a mole in a certain spot on the cheek of a woman was considered fashionable. These were called "beauty marks." Some were even painted on. However, not all moles are beautiful. They can be raised from the skin and very noticeable, they may contain dark hairs, or they may be dangerous.
Moles can appear anywhere on the skin. They are usually brown in color but can be skin colored and various sizes and shapes. The brown color is caused by melanocytes, special cells that produce the pigment melanin. Moles probably are determined before a person is born. Most appear during the first 20 years of life, although some may not appear until later. Sun exposure increases the number of moles, and they may darken. During the teen years and pregnancy, moles also get darker and larger and new ones may appear. Each mole has its own growth pattern. The typical life cycle of the common mole takes about 50 years. At first, moles are flat and tan like a freckle, or they can be pink, brown or black in color, Over time, they usually enlarge and some develop hairs. As the years pass, moles can change slowly, becoming more raised and lighter in color. Some will not change at all. Some moles will slowly disappear, seeming to fade away. Others will become raised far from the skin. They may develop a small "stalk" and eventually fall off or are rubbed off.
Recent studies have shown that certain types of moles have a higher-than-average risk of becoming cancerous. They may develop into a form of skin cancer known as malignant melanoma. Sunburns may increase the risk of melanoma. People with many more moles than average (greater than 100) are also more at risk for melanoma.
Moles are present at birth in about 1 in 100 people. They are called congenital nevi. These moles may be more likely to develop a melanoma than moles which appear after birth. Moles known as dysplastic nevi or atypical moles are larger than average (usually larger than a pencil eraser) and irregular in shape. They tend to have uneven color with dark brown centers and lighter, sometimes reddish, uneven border or black dots at edge. These moles often run in families. People with dysplastic nevi may have a greater chance of developing malignant melanoma and should be seen regularly by a dermatologist to check for any changes that might indicate skin cancer. Those susceptible should also learn to do regular self-examinations, looking for changes in the color, size or shape of their moles or the appearance of new moles. Sunscreen and protective clothing should be used to shield moles from sun exposure. Recognizing the early warning signs of malignant melanoma is important. Remember the ABCDs of melanoma when examining your moles: Read more here for Dr. Robinson in the News on Moles.

